| Magyar verzió |
|||
| News | |||
|
|||
| Standard | |||
| Origin, character | |||
| Articles, infos | |||
| Photo album | |||
|
|||
| Breeders | |||
| Puppies | |||
| Stud dogs | |||
| Genetic diseases | |||
|
|||
| Show results | |||
| Show schedules | |||
| Show photos | |||
| Champion titles | |||
|
|||
| Links | |||
| Guestbook | |||
| Contact | |||
| GENETIC PROBLEMS OF THE TIBETAN TERRIER |
| INFO | |||||||
The Tibetan is a very hardy breed and is considered long-lived with most living well beyond 12 years and many to 15 or 16 years. Some problems found in the Tibetan Terrier are: hip dysplasia (HD), patella luxation (PL), progressive retinal atrophy (PRA), lens luxation (LL), hypo-thyroidism, cataracts and canine neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CCL/NCL). Some of these problems have been proven to be hereditary, and conscientious breeders have screened their stock and can explain these problems and their incidence. Many breeders will have knowledge of their puppies’ bloodlines and potential buyers are advised to ask questions and inquire as to evidence of any testing done on the sire and dam. Click on the problem's name to read about it. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| PATELLA LUXATION | |||||||
The patella, or kneecap, is part of the stifle joint (knee). In patellar luxation, the kneecap luxates, or pops out of place, either in a medial or lateral position. Bilateral involvement is most common, but unilateral is not uncommon. Animals can be affected by the time they are 8 weeks of age. The most notable finding is a knock-knee (genu valgum) stance. The patella is usually reducible, and laxity of Although the luxation may not be present at birth, the anatomical deformities that cause these luxations are present at that time and are responsible for subsequent recurrent patellar luxation. Patellar luxation should be considered an inherited disease. Three classes of patients are identifiable: 1, Neonates and older puppies often show clinical signs of abnormal hind-leg carriage and function from the time they start walking; these present grades 3 and 4 generally. 2, Young to mature animals with grade 2 to 3 luxations usually have exhibited abnormal or intermittently abnormal gaits all their lives but are presented when the problem symptomatically worsens. 3, Older animals with grade 1 and 2 luxations may exhibit sudden signs of lameness because of further breakdown of soft tissues as result of minor trauma or because of worsening of degenerative joint disease pain. Signs vary dramatically with the degree of luxation. In grades 1 and 2, lameness is evident only when the patella is in the luxated position. The leg is carried with the stifle joint flexed but may be touched to the ground every third or fourth step at fast gaits. Grade 3 and 4 animals exhibit a crouching, bowlegged stance (genu varum) with the feet turned inward and with most of the weight transferred to the front legs. Permanent luxation renders the quadriceps ineffective in extending the stifle. Extension of the stifle will allow reduction of the luxation in grades 1 and 2. Pain is present in some cases, especially when chondromalacia of the patella and femoral condyle is present. Most animals; however, seem to show little irritation upon palpation. source: OFA |
|||||||
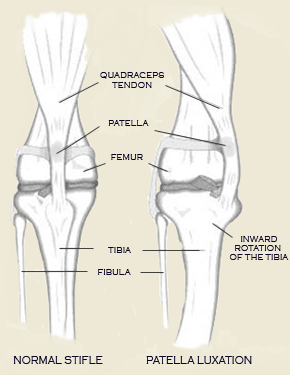 the medial collateral ligament may be evident. The medial retinacular tissues of the stifle joint are often thickened, and the foot can be seen to twist laterally as weight is placed on the limb.
the medial collateral ligament may be evident. The medial retinacular tissues of the stifle joint are often thickened, and the foot can be seen to twist laterally as weight is placed on the limb.